*colored icons can be clicked, black icons mean that the file is not available yet
Bulk polymerization
A polymerization technique typically using a liquid monomer to synthesize a polymer using free radicals as initiators.
For example – synthesis of polystyrene. The initiator should dissolve the monomer. The monomer units can then be propagated into chains before the termination. This process is very exothermic, and the polymer obtained is pure.
Emulsion polymerization
Also a free-radical initiated polymerization but the monomers are now in an emulsion of water.
For example – synthesis of a type of rubber/latex, polyisobutadiene. The process starts with water, monomers, and a surfactant which prevents coagulation. This process can result in high molecular weight polymers, but the surfactants and other additives are typically difficult to remove.
Gel permeation chromatography (GPC)

PCO.edge Camera

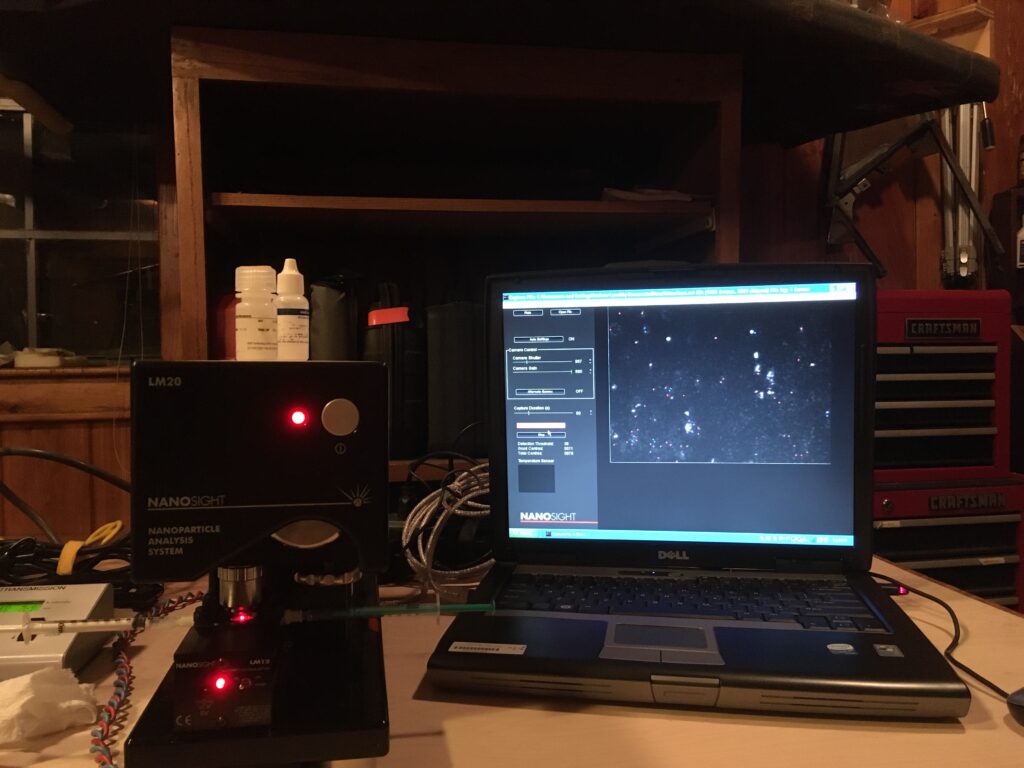
Simultaneous Multi-Angle Light Scattering (SMALS)
The SMALS apparatus is unique in all the world. Built at Georgia Tech around a Wyatt DAWN EOS multiangle light scattering apparatus, it features a 50 mW solid state laser operating at 685 nm, eight channels optimized for static light scattering (SLS) and eight channels for dynamic light scattering (DLS). The SLS channels use traditional Wyatt diode detectors at different angles (XXX-XXX degrees). These detectors are designed to collect spatially incoherent light, as optimal for the SLS experiment. For DLS, eight separate single-mode optical fibers are arranged at various angles. They carry spatially coherent light to 8 Excelitas avalanche photodiode detector modules which in turn drive an ALV wide-range multicorrelator (correlation times of 250 ns to > 1 s). The SLS and DLS detectors operate simultaneously so that evolving systems can be studied (examples: polymerization or degradation of polymer latex particles or silica spheres; attack by antimicrobial peptides on liposomes). Such kinetic light scattering experiments can be conducted with a time resolution of about 125 ms for SLS. For DLS, the kinetic time resolution is dictated by the sample itself but 10-s resolution is achievable in some circumstances. By combining the SLS and DLS data, one can obtain the ratio of gyration to hydrodynamic radius, ρ = Rg/Rh.
Density and Sound Velocity Meter

Asymmetric Flow Field Flow Fractionation (AF4)
- Robust separation of macromolecules and nanoparticles from 1 nm to 1000 nm with excellent resolution
- No stationary phase – open channel separation with minimal shear and surface interactions
- Versatile choice of separation channels, permitting sample loads from µL to mL, including semi-preparative FFF
- Optimize separation methods to enhance resolution or size range simply by adjusting flow ratios, even programmatically during a run
- Fractions can be collected and used for off-line analysis (with electron microscopy, MS, ICP-MS, ELISA, etc.)
- Typical analysis times 10 – 30 minutes
- Utilize the fritless column for aggregation-prone samples
- Make use of the highest quality HPLC pumps and autosamplers from Agilent, Shimadzu, Thermo, or Waters
Gel Electrophoresis
Disk Centrifuge
Small Angle Light Scattering
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
TGA measures the weight of a substance as its heated – you can heat up to temperatures as high as 800 C or even above. By this temperature organic substances burn away completely. TGA can measure weights with great accuracy and is useful in determining the loss of gases at various key temperatures. This provides information about the composition of the material.

Baby Leitz (Kohler Illumination)
Lisa is a versatile polarized and fluorescence light microscope. The old girl was not designed for infinity corrected objectives, but she has been heavily face-lifted with modern light sources. She can be used with modern cameras, usually the Canon EOS 6D but also others are possible. Lisa is delightful and a good choice to practice your Kohler illumination skills (see Kodak book, Photography Through the Microscope).